Diabetes Specialist - DIABETES COMPLICATIONS
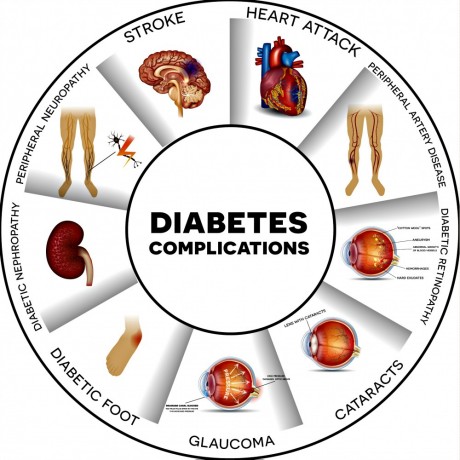
5 years ago - Services - Lahore - 6.2K viewsDiabetes mellitus can cause complications in almost all the systems of the body if it is poorly controlled. Our main aim is to keep blood glucose and HbA1c at levels equal to that of normal population in order to prevent development of complications. Almost all the complications of diabetes are due to ‘’microangiopathy’’ that is damage to small blood vessels reducing blood supply to different organs of the body.
Eye Complications:
After 10-15 years of poorly controlled diabetes, eye complications tend to develop. Eye complications are more common in type 1 than in type 2 diabetes. These include:
1. InfectionsHigh blood glucose level makes the eye prone to bacterial over growth and infections including stye ( infection of eye lashes and lids) or conjunctivitis ( infection of conjunctiva- the membrane covering the eye)
2. Glaucoma: In urdu it is known as ‘’ kalamotia’’. It is increased pressure in the eyeball due to excessive fluid production or inadequate drainage of this fluid. If untreated it can lead to blindness. At initial stage it is treated with various eye drops. At later stages surgery may be required to drain excess fluid.
Patient should have periodic eye examination and measurement of eye pressure.
3. Cataract: It is known as ‘’sufaidmotia’’ in urdu. It is disease of lens of the eye which becomes opaque due to protein deposits. It will cause obstruction of vision. At initial stages it can be handled by wearing anti-glare lens spectacles or sunglasses. but when lens is completely effected by cataract, surgery is done to remove the lens and place an artificial lens in its place.
4. Retinopathy: Retina is the inner most layer of the eyeball. It is most important for vision. In almost all diabetics some changes occur in blood vessels of retina gradually. Initial stage is called ‘’background or non-proliferative retinopathy’’ in which blood vessels balloon up or form pouches. It causes no symptoms, it can be detected by ophthalmologist on routine visit.
Later stage is proliferative retinopathy in which blood leaks from weak blood vessels, and new fragile blood vessels are formed which are more prone to hemorrhage. At this stage patient may feel diminishing vision. The best treatment for this stage is laser photocoagulation that seals the blood vessels to prevent further bleeding. There may be transient blurring of vision after laser surgery for few days, and there can be permanently decreased peripheral vision after surgery.
Kidney
Kidneys are vital organs for excretion of all the toxic waste from the body. They have a very rich blood supply which helps in filtering all the wastes from the blood. Poorly controlled and long standing diabetes cause damage to these blood vessels that is break down of this filter. As a result toxins are not properly filtered out and useful substances like proteins are lost in the urine. High blood pressure along with high glucose level further aggravated the kidney damage. There are following stages of progression of kidney disease.
1. Microalbuminuria: The initial stage when small sized proteins leak out of urine. It causes no symptoms and can be treated with tight blood glucose control and medicines like ACE inhibitors
2. Macroalbuminuria: The second stage in which large size proteins are also filtered out in urine. It can rapidly progress to end stage renal disease. Low protein diet and good control of blood pressure and blood glucose is required. Frequent urine and blood test to check levels of toxins, urea and creatinin in the blood. Consult a nephrologist at this stage.
3. End-stage renal disease: The stage when the kidneys fail to function. There will be edema (swelling) of feet and whole body due to water retention. Urea and creatinin will rise in the blood giving rise to symptoms of uremia like nausea, vomiting, headache, agitation, confusion, drowsiness or coma. At this stage patient is referred to nephrologist for dialysis or transplant. At end stage blood sugar usually tends to be low and dose of insulin will have to be reduced.
Treatment:
- At initial stage control of blood glucose and blood pressure
- Restriction in dietary protein and fluids
- Exercise
- ACE inhibitors and ARB group of medicines, these medicines lower the blood pressure and prevent damage to kidney membranes and filter.
- Dialysis, peritoneal or hemodialysis is a process to remove toxic wastes from the blood by passing through a filtering machine twice or thrice a week.
- Kidney transplant is the last stage when kidney has completely failed, a new kidney can be transplanted but it has its own problems and risks. (discussed in transplant section)